InterFoam Solver for 2 incompressible, isothermal immiscible fluids using a VOF
(volume of fluid) phase-fraction based interface capturing approach, with optional mesh motion and mesh topology changes including adaptive re-meshing.
Contents
1 Related information in the web
1.1 Online discussion
- VOF method
- About interFoam solver
- How to set the two parameters of solver 'interFoam'?
- Inlet in interFoam (recovered via web.archive.org)
- Question about interface flow and adaptive mesh - In this thread Henry Weller explains how interFoam is different from the CICSAM method.
1.2 Useful links
An overview about interfoam: http://infofich.unl.edu.ar/upload/3be0e16065026527477b4b948c4caa7523c8ea52.pdf
2 Equations
The solver solves the Navier Stokes equations for two incompressible, isothermal immiscible fluids. That means that the material properties are constant in the region filled by one of the two fluid except at the interphase.
2.1 Continuity Equation
The constant-density continuity equation is
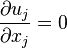 | (1) |
2.2 Momentum Equation
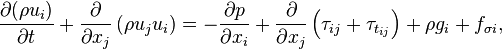 | (2) |
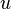 represent the velocity,
represent the velocity, 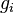 the gravitational acceleration,
the gravitational acceleration, 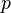 the pressure and
the pressure and
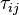 and
and 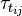 are the viscose and turbulent stresses.
are the viscose and turbulent stresses. 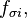 is the
surface tension.
is the
surface tension.
The density 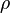 is defined as follows:
is defined as follows:
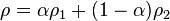 | (3) |
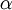 is 1 inside fluid 1 with the density
is 1 inside fluid 1 with the density 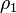 and 0 inside fluid 2 with the density
and 0 inside fluid 2 with the density 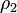 . At the interphase between
the two fluids
. At the interphase between
the two fluids 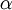 varies between 0 and 1.
varies between 0 and 1.
The surface tension 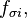 is modelled as continuum surface force (CSF)[1]. It is calculated as follows (see also [2]):
is modelled as continuum surface force (CSF)[1]. It is calculated as follows (see also [2]):
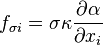
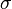 is the surface tension constant and
is the surface tension constant and 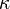 the curvature. The curvature can be approximated as follows [3] and [4]:
the curvature. The curvature can be approximated as follows [3] and [4]:
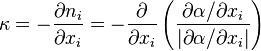
2.3 Equation for the interphase
In order to know where the interphase between the two fluids is, an additional equation for 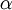 has to be solved.
has to be solved.
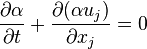 | (4) |
The equation can be seen as the conservation of the mixture components along the path of a fluid parcel.
3 Source Code
\\OpenFOAM 6
3.1 interFoam.C
#include "fvCFD.H" #include "dynamicFvMesh.H" #include "CMULES.H" #include "EulerDdtScheme.H" #include "localEulerDdtScheme.H" #include "CrankNicolsonDdtScheme.H" #include "subCycle.H" #include "immiscibleIncompressibleTwoPhaseMixture.H" #include "turbulentTransportModel.H" #include "pimpleControl.H" #include "fvOptions.H" #include "CorrectPhi.H" #include "fvcSmooth.H" // * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * // int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { #include "postProcess.H" #include "setRootCaseLists.H" #include "createTime.H" #include "createDynamicFvMesh.H" #include "initContinuityErrs.H" #include "createDyMControls.H" #include "createFields.H" #include "createAlphaFluxes.H" #include "initCorrectPhi.H" #include "createUfIfPresent.H" turbulence->validate(); if (!LTS) { #include "CourantNo.H" #include "setInitialDeltaT.H" } // * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * // Info<< "\nStarting time loop\n" << endl; while (runTime.run()) { #include "readDyMControls.H" if (LTS) { #include "setRDeltaT.H" } else { #include "CourantNo.H" #include "alphaCourantNo.H" #include "setDeltaT.H" } runTime++; Info<< "Time = " << runTime.timeName() << nl << endl; // --- Pressure-velocity PIMPLE corrector loop while (pimple.loop()) { if (pimple.firstIter() || moveMeshOuterCorrectors) { mesh.update(); if (mesh.changing()) { // Do not apply previous time-step mesh compression flux // if the mesh topology changed if (mesh.topoChanging()) { talphaPhi1Corr0.clear(); } gh = (g & mesh.C()) - ghRef; ghf = (g & mesh.Cf()) - ghRef; MRF.update(); if (correctPhi) { // Calculate absolute flux // from the mapped surface velocity phi = mesh.Sf() & Uf(); #include "correctPhi.H" // Make the flux relative to the mesh motion fvc::makeRelative(phi, U); mixture.correct(); } if (checkMeshCourantNo) { #include "meshCourantNo.H" } } } #include "alphaControls.H" #include "alphaEqnSubCycle.H" mixture.correct(); #include "UEqn.H" // --- Pressure corrector loop while (pimple.correct()) { #include "pEqn.H" } if (pimple.turbCorr()) { turbulence->correct(); } } runTime.write(); Info<< "ExecutionTime = " << runTime.elapsedCpuTime() << " s" << " ClockTime = " << runTime.elapsedClockTime() << " s" << nl << endl; } Info<< "End\n" << endl; return 0; } // ************************************************************************* //
4 References
- ↑ Brackbill, J. U., Douglas B. Kothe, and Charles Zemach. "A continuum method for modeling surface tension." Journal of computational physics 100.2 (1992): 335-354.
- ↑ Heyns, Johan A., and Oliver F. Oxtoby. "Modelling surface tension dominated multiphase flows using the VOF approach." 6th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics. 2014.
- ↑ Brackbill, J. U., Douglas B. Kothe, and Charles Zemach. "A continuum method for modeling surface tension." Journal of computational physics 100.2 (1992): 335-354.
- ↑ Heyns, Johan A., and Oliver F. Oxtoby. "Modelling surface tension dominated multiphase flows using the VOF approach." 6th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics. 2014.